Staking in simple words is a way to verify transactions made using crypto and earn rewards through a participant’s holdings. Staking means committing coins to one blockchain network to confirm transactions. It occurs in the cryptocurrencies that adopt the Proof of Stake model to carry out a payment. Staking is often considered to be one of the easiest ways to gain passive income because of the varying interest rates that are offered by different currencies. Those who stake their cryptocurrencies are known as ‘validators’. For staking their coins the validators are rewarded with new coins from the network that is created.
What is Staking?
By staking some of the holdings, it is possible to earn rewards over time through an offered percentage rate which works very similar to an interest-based savings account in banks. Unlike banks, crypto staking works a little differently, where the Proof of Stake, also known as consensus mechanism, is applied in every transaction made as a result of which there is no third party control or involvement, and each transaction is verified. The Proof of Stake, also known as consensus mechanism, is applied in every transaction made as a result of which there is no third party control or involvement.
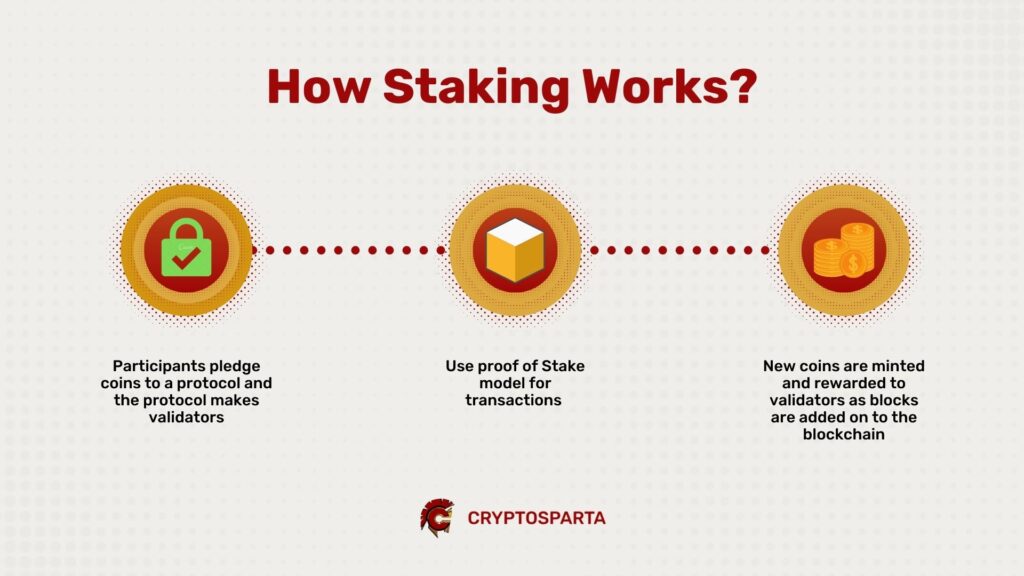
How does Staking work?
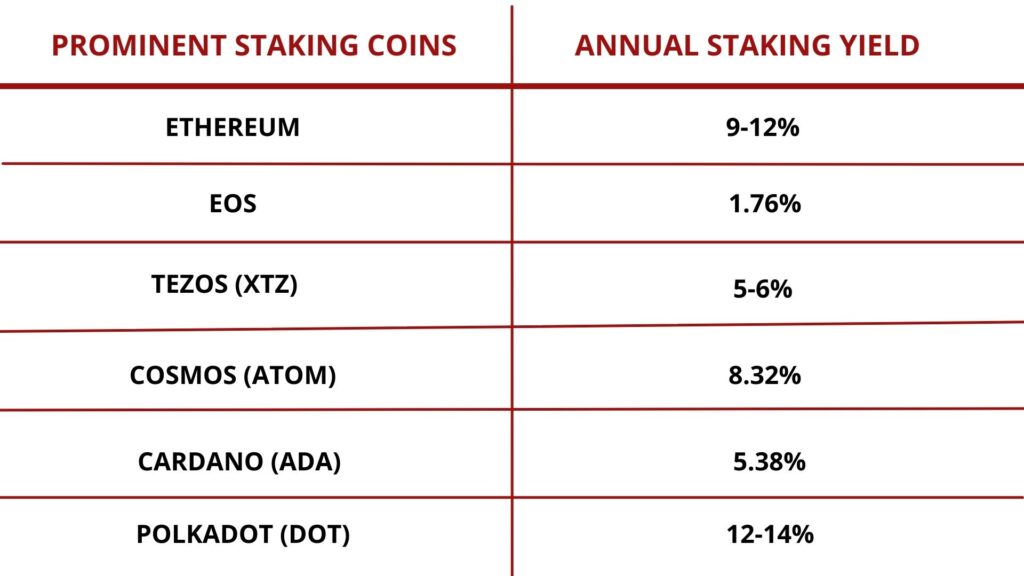
Validators who invest their coins are selected randomly by a series of protocols at a specified interval so as to create a block. Oftentimes, validators who have invested more coins tend to be selected sooner than the ones with smaller investments. The ‘stake’ motivates validators to maintain the security of the chain. With the addition of a new block, they are rewarded with the new coins that are minted. Usually, the rewards are paid in the same token they have invested in but certain cryptocurrencies can pay rewards in a second token as well. For calculating staking rewards, there is no fixed method. Each blockchain calculates the reward differently by taking into consideration various factors such as
- The number of coins being staked by the validator
- How actively the validator has been staking
- The inflation rate
- The total coins in the blockchain.
Staking is seen to be profitable as a person doesn’t need to do much in the entire process except that of investing his crypto/coin and letting it sit there for some time to earn a good profit. The longer the person stakes the coin, the higher is the profit. The rewards are determined by intrinsic factors such as the size of the staking pool, the amount of locked supply, and the size of the block reward. The staking pool is a group of coin chain holders who merge resources to validate blocks and thus increase rewards. Another feature of staking is the ‘Lockup Period’ or ‘Vesting’ where the invested crypto cannot be transferred for a certain amount of time and a person cannot trade or shift as long as the vesting period goes on.
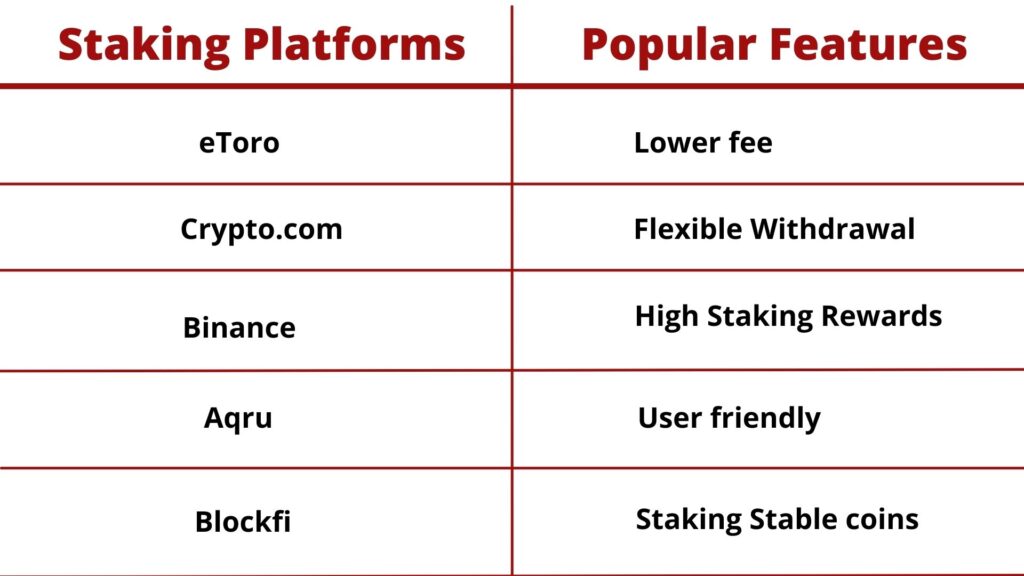
The advantages of staking is that it is the easy way to earn high profits through interest and unlike mining, staking does not require additional equipment for the cryptography problems and thus becomes environment friendly. Most importantly, staking provides security and efficiency to a blockchain a person invests in and stakers have voting rights in the blockchain network.
Why only certain cryptocurrencies don’t offer Staking?
The most famous cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, does not offer the option of staking majorly because of the simple bank-like model of transactions it follows. Proof of Work becomes a difficult process because of the numerous activities that go on resulting in higher fees and longer time consumption for each transaction.
The model functions like a competition where cryptographic puzzles, also known as ‘mining’ are put up for the ‘miners’ who compete in solving the presented mathematical tasks. The one who solves the puzzle first is given the right to add the newest block of the transactions that have been verified onto the blockchain. As a result of this, the miner is rewarded with some fee. Because it is a long process and can cost more than the usual fee, a lot of cryptocurrencies do not offer the option of staking.

How is Staking different from Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining?
The three prospects of DeFi trading are notably different from each other with their own set of profits and risks. Essentially while staking is locking of crypto assets to a blockchain for being selected as a validator using the Proof Of Stake consensus algorithm, yield farming refers to locking crypto assets in blockchain protocols using automated market makers technology and liquidity mining means to add assets to liquidity pools of DeFi protocols using Smart Contracts and Liquidity providers. All three tradings have a different set of rewards for the investors. Staking gets rewards in native tokens (in most cases) along with the privilege of validating transactions, yield farming provides APY rewards on assets locked by the participant and liquidity mining provides rewards in the form of LP tokens or GOV tokens. In totality, all three methods put idle crypto to work. Staking creates a safer blockchain while yield farming tries to get the highest yield possible and liquidity mining tries to provide liquidity to DeFi protocols.

Conclusion
All available methods of trading come with their own set of benefits and risks, it is always advised to do all technical research required to understand the best option available to a participant. Thus, it is important to analyze all possible risks and market status before staking any cryptocurrency to avoid major loss.
About me
Hi, I am Zainab. I am a student of English Literature. I am intrigued by the development of virtual currency and want to explore more in the field. In my free time, I like to read and try new food recipes.











